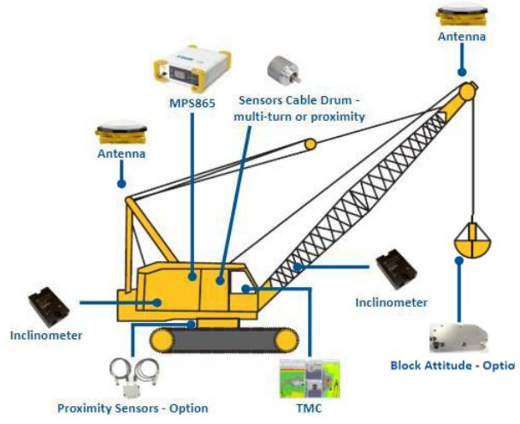
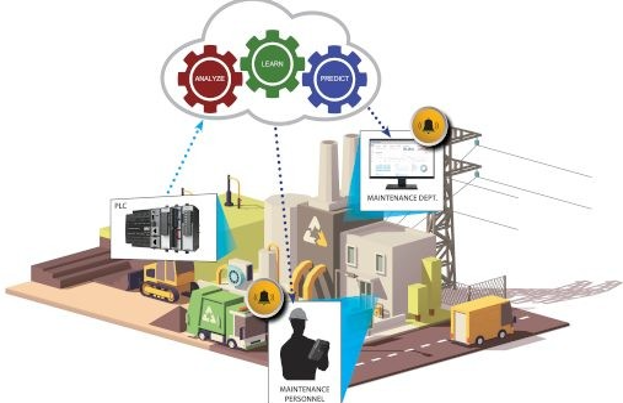
PLANT AUTOMATION
Overview
Industrial automation is the use of control systems, such as computers or robots, and information technologies for handling different processes and machinery in an industry. It aims to improve productivity, quality, safety, and flexibility while reducing the need for human intervention. Here are some key aspects:
What we do
1. Process Control
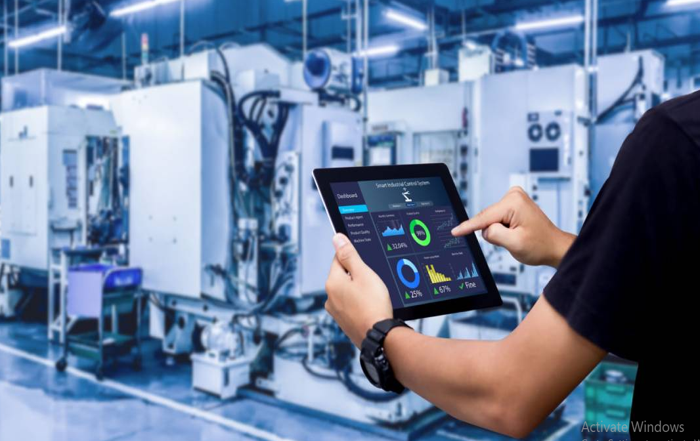
Automation systems monitor and control processes in manufacturing and production, ensuring consistency and precision. Examples include SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and DCS (Distributed Control Systems).
2. Robotics
Robots are widely used for repetitive, high-precision tasks, such as assembly, painting, and welding, particularly in automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery industries.
3. PLC and HMI
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) are the backbone of automation. PLCs are used to control machinery, while HMIs allow operators to interact with the system.
4. Machine Vision
Machine vision systems use cameras and image processing for inspection, measurement, and quality control, helping identify defects and ensure quality.
5. AI and IoT
Integrating AI and the Internet of Things (IoT) enables predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and data analytics, which helps industries make better decisions and improve efficiency.
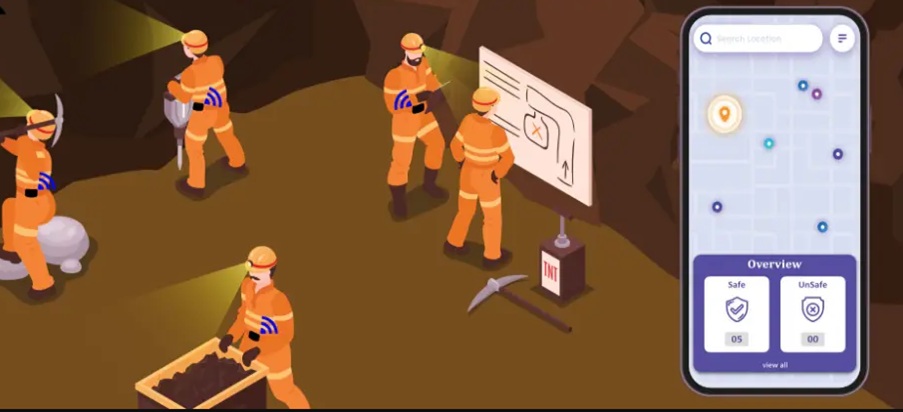
6. Safety Systems
Automated safety systems, such as emergency stop buttons and light curtains, protect workers by halting machinery when unsafe conditions are detected